Correctly Label the Anatomical Elements of the Tongue.
1 Answer to 9 Correctly label the anatomical elements of a taste bud. 4105png - Correctly label the anatomical elements of the tongue.
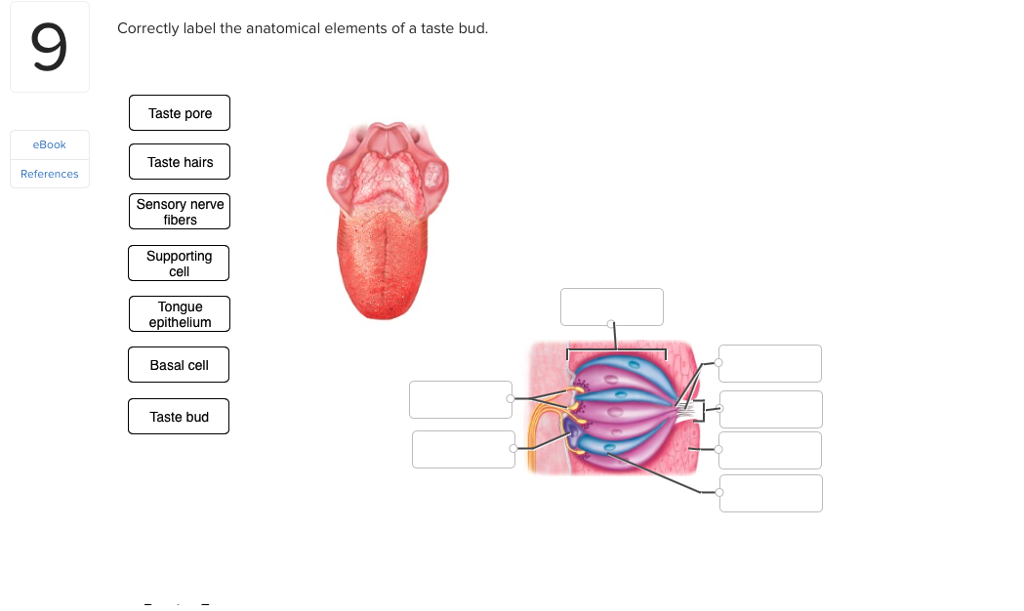
Solved 9 Correctly Label The Anatomical Elements Of A Taste Chegg Com
Correctly identify the following extrinsic muscles of the eyeball.
. The boundary between them is marked by a Vshaped row of vallate papillae and behind these a. Correctly identify the following structures of the eye. Epithelium muscles and glands.
Correctly label the anatomical elements of the projection pathways for pain. The epithelium is stratified and non-cornified. In this article we shall explore the structure of the.
Anterior two-thirds of the tongue Facial nerveVII 2. 95 is made up of three elements. Thousands of taste buds.
Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. Correctly label the anatomical elements of the tongue. Origin - root of tongue body of hyoid bone Insertion - apex of tongue Innervation - hypoglossal nerve CN XII Blood supply - lingual branch of external carotid artery Action - retracts and broadens tongue lowers apex of tongue.
The tongue is an organ responsible for the manipulation of food during the process of chewing also called mastication. Anatomy and Physiology Correctly label the following anatomical features of the tongue. Hence you cannot taste or smell food when you have a fever or cold.
And the posterior onethird the root occupies the oropharynx. Read each description or phrase below regarding sound waves. The posterior surface is made up entirely of the root.
Start studying Correctly label the anatomical elements of a taste bud. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Origin - lingual septum Insertion - lateral margin of tongue.
Tiny bumps called papillae give the tongue its rough texture. Taste gustatory cells are more or less bananashaped and have a tuft of apical microvilli called taste hairs which serve as receptor surfaces for taste molecules. The tongue is covered with moist pink tissue called mucosa.
Taste buds are lemonshaped groups of 50 to 150 taste cells supporting cells and basal cells. The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. Adjust credit for all students.
This anatomical review focuses on structure function relationships and diseases affecting the tongue. The free surface comprises short taste hair. 96 and the taste buds.
The visible bumps on the tongue are not taste buds but lingual papillaeFiliform papillaeare the most abundant papillae on the humantongue but they are small and play no gustatory roleFoliate papillaeform parallel ridges on the sides of the tongue about twothirds of the way back from the tip adjacent to the. The tongues upper surface is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. Some choices may be used more than once or not at all.
The tongue is made up of three elements. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. Two types of special structures are seen on it.
Primary somesthetic cortex Somesthetic association area Thalamus Spinoreticular tract Spinothalamic tract First-order nerve fiber Hypothalamus Third-order nerve fibers Reticular Formation Anterolateral system Second-order. Correctly label the anatomical elements of the taste bud. The top of the tongue superior surface has a V-shaped line known as the terminal sulcus that divides the tongue into the anterior and posterior surfaces.
Taste pore eBook Taste hairs References Sensory nerve fibers Supporting cell Tongue epitheliunm Basal cell Taste buo. They are lined by squamous epithelial tissue and have a broad bottom. The taste cells are slender rod-shaped with a nucleus in the centre.
The tongue a voluntary muscular structure is attached by a fold called the frenulum to the floor of the mouth. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process and is the primary organ of taste. Typically between 8 and 12 circumvallate papillae are arranged in an inverted V-shape towards the base of the tongue.
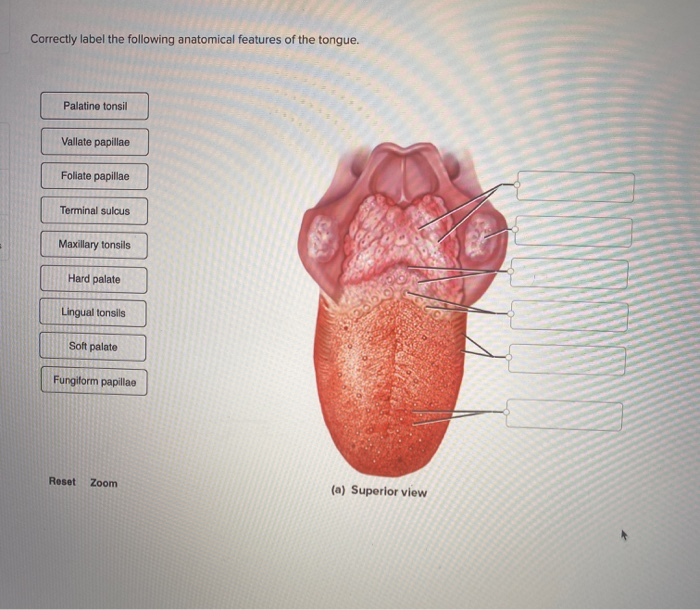
The anterior twothirds of the tongue called the body occupies the oral cavity. Sounds that are made with the tongue body. Correctly label the following anatomical features of the tongue.
Start with the cornea at the top. Correctly label the anatomical elements of a taste bud. The large mass of the tongue in the back of the mouth is the tongue body often also called the dorsum from the Latin word for back as in the dorsal fin of a shark ie the fin on its back.
Moreover it is also responsible for the sensation of taste along with the nose. Posterior one-third of the tongue and the superior pharynx Glossopharyngeal nerve IX 3. The taste buds help to sense taste.
In this article we will discuss about the anatomical structure of human tongue with the help of suitable diagrams. The anterior surface is made up of the apex at the tip and body. Then click and drag each into the appropriate category based on whether it is associated with pitch or loudness.
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth. Correctly label the anatomical elements of the tongue. Indicate whether the given structure is located in.
Foliate papillae Epiglottis Lingual tonsil Epiglottis Palatine tonsil Lingual Course Hero. In order not to get confused over which part the term back refers to think of the tongue as an animal. 1st molar Mandible Styloglossus m.
The epithelium comprises papillae and taste buds. Jul 14 2021 0326 PM. Taste pore eBook Taste hairs References Sensory nerve fibers Supporting cell Tongue epitheliunm Basal cell Taste buo.
Correctly label the anatomical elements of the tongue. Match the taste sensation to the chemical trigger.
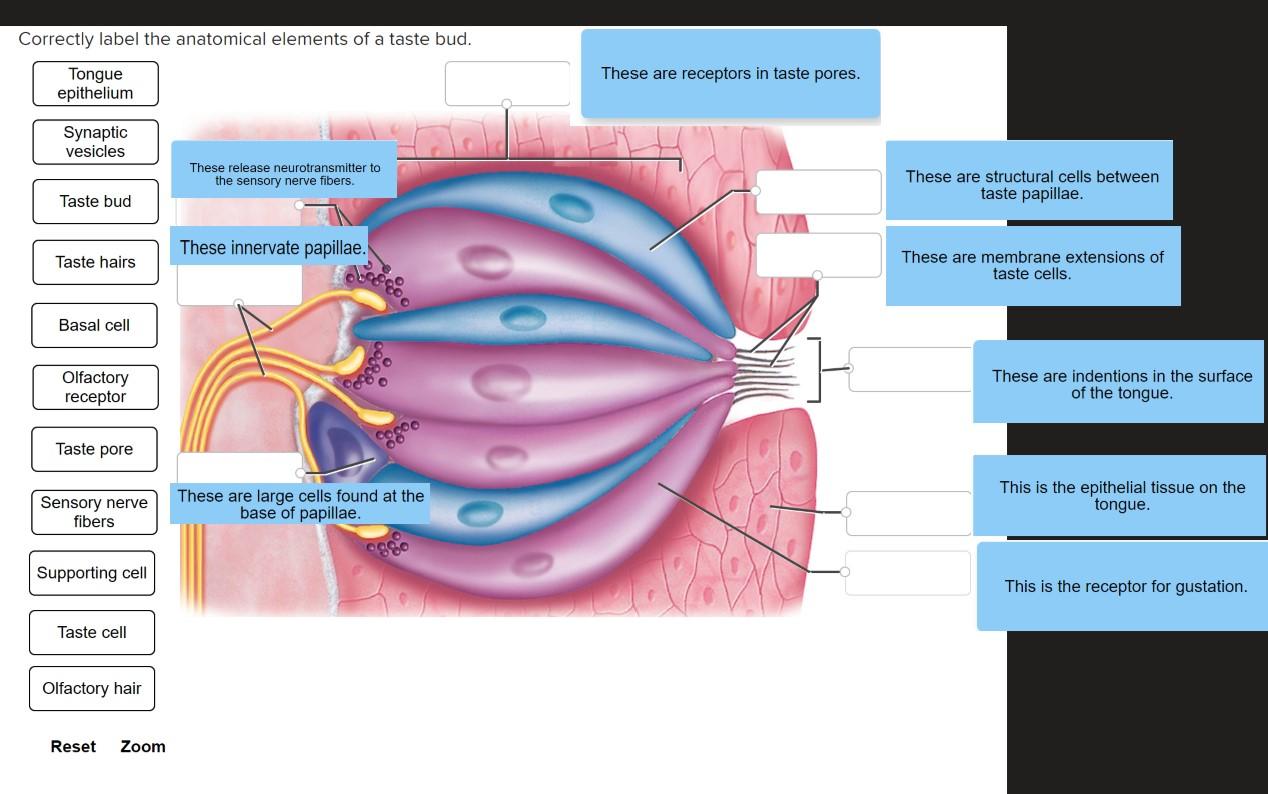
Solved Correctly Label The Anatomical Elements Of A Taste Chegg Com

Senses Worksheet Flashcards Quizlet
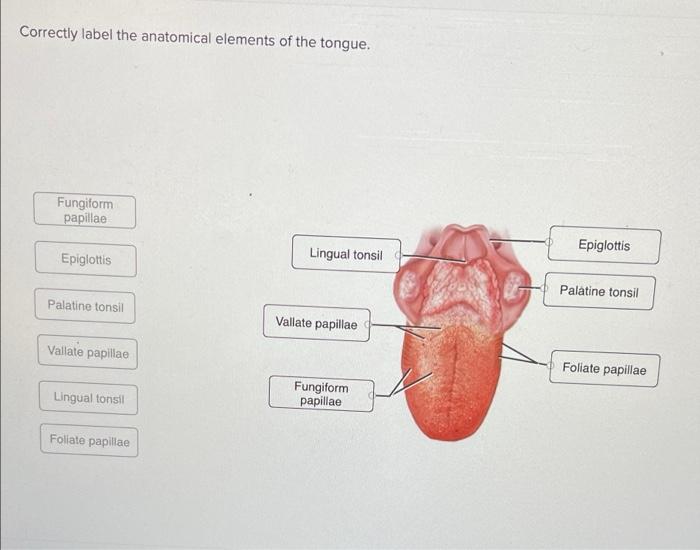
Solved Sory System I Saved Help Save Exit Submit Drag Each Chegg Com

Solved Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment